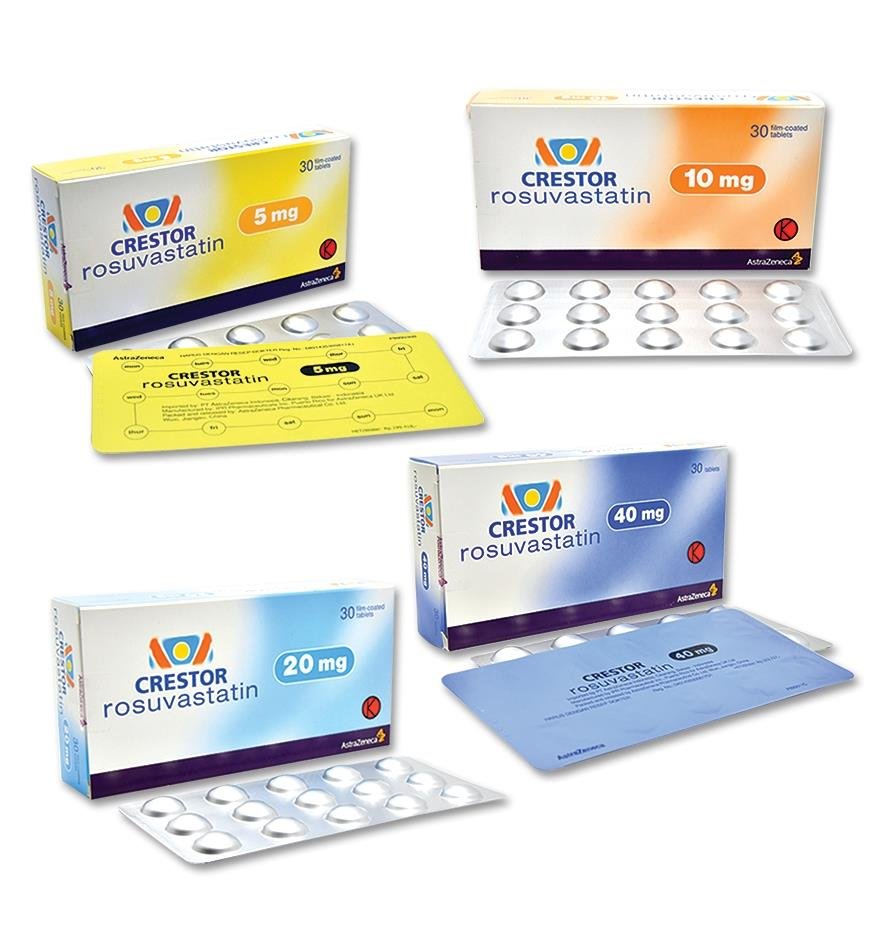
Crestor
Crestor - 20mg
| Product | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 pills | $2.97 | $89.15 | Buy Now | |
| 60 pills | $2.22 | $45.13 | $178.29 $133.16 | Buy Now |
| 90 pills | $1.97 | $90.26 | $267.44 $177.18 | Buy Now |
| 120 pills | $1.84 | $135.39 | $356.59 $221.20 | Buy Now |
| 180 pills | $1.72 | $225.66 | $534.89 $309.23 | Buy Now |
| 270 pills | $1.63 | $361.05 | $802.33 $441.28 | Buy Now |
Crestor - 10mg
| Product | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 pills | $1.95 | $58.35 | Buy Now | |
| 60 pills | $1.52 | $25.60 | $116.70 $91.10 | Buy Now |
| 90 pills | $1.38 | $51.21 | $175.07 $123.86 | Buy Now |
| 120 pills | $1.31 | $76.81 | $233.42 $156.61 | Buy Now |
| 180 pills | $1.23 | $128.01 | $350.12 $222.11 | Buy Now |
| 270 pills | $1.19 | $204.82 | $525.18 $320.36 | Buy Now |
Crestor - 5mg
| Product | Per Pill | Savings | Per Pack | Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 pills | $1.07 | $32.06 | Buy Now | |
| 60 pills | $0.83 | $14.34 | $64.12 $49.78 | Buy Now |
| 90 pills | $0.75 | $28.68 | $96.17 $67.49 | Buy Now |
| 120 pills | $0.71 | $43.01 | $128.22 $85.21 | Buy Now |
| 180 pills | $0.67 | $71.69 | $192.34 $120.65 | Buy Now |
| 270 pills | $0.64 | $114.70 | $288.51 $173.81 | Buy Now |
| 360 pills | $0.63 | $157.72 | $384.68 $226.96 | Buy Now |
Overview of Crestor
1. General Introduction
Crestor (rosuvastatin) is a potent statin medication extensively used for lowering cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. By inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, Crestor effectively reduces cholesterol production in the liver, thereby helping to prevent atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular conditions. This overview will explore the primary uses, benefits, efficacy, safety, and dosing convenience of Crestor, offering valuable insights for both patients and healthcare providers.
2. Primary Purpose
Crestor is primarily prescribed to manage elevated cholesterol levels, specifically targeting low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. Additionally, it is used to elevate high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels. By effectively managing these lipid levels, Crestor plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events in patients with hyperlipidemia or mixed dyslipidemia. Furthermore, Crestor is often prescribed to individuals with familial hypercholesterolemia, a genetic disorder characterized by abnormally high cholesterol levels.
3. Key Benefits and Properties
Crestor provides multiple benefits, making it a highly effective and versatile medication:
- Cholesterol Reduction: Crestor significantly lowers LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while boosting HDL cholesterol levels, thus promoting a healthier lipid profile.
- Cardiovascular Risk Reduction: By effectively managing cholesterol levels, Crestor reduces the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events, preventing the progression of atherosclerosis.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Crestor has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to overall cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation in the blood vessels.
- Pleiotropic Effects: Beyond cholesterol reduction, Crestor enhances endothelial function and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques, offering additional cardiovascular protection.
4. Efficacy
Numerous clinical studies confirm Crestor’s efficacy in managing cholesterol levels and reducing cardiovascular risk. Research indicates that Crestor can lower LDL cholesterol levels by up to 50% in many patients, resulting in substantial improvements in their lipid profiles. Additionally, Crestor has proven effective in decreasing the incidence of cardiovascular events, making it a reliable long-term option for managing hyperlipidemia and related conditions.
5. Safety and Tolerability
Crestor is generally well-tolerated, with a favorable safety profile. Common side effects include headache, muscle pain, abdominal pain, weakness, and nausea. These side effects are typically mild and transient, but patients should report any persistent or severe symptoms to their healthcare provider. Rare but serious side effects, such as muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis) and liver damage, require immediate medical attention. Regular monitoring of liver enzymes and kidney function is recommended during Crestor therapy to ensure safety.
6. Convenience of Dosing
Crestor offers flexible dosing options, typically taken once daily, with or without food. The starting dose generally ranges from 5 mg to 10 mg, depending on the patient’s condition and response to treatment. The dose can be adjusted according to individual needs, with a maximum recommended dose of 40 mg per day. This flexibility allows for personalized treatment plans that optimize efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Indications for Use of Crestor
1. Conditions Treated by Crestor
Crestor (rosuvastatin) is primarily indicated for treating hyperlipidemia, mixed dyslipidemia, and familial hypercholesterolemia. It is also prescribed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with elevated cholesterol levels and other associated risk factors.
2. Symptoms and Indications
- Hyperlipidemia: Crestor effectively lowers high levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing HDL cholesterol, thereby improving overall lipid profiles.
- Mixed Dyslipidemia: Crestor helps manage mixed dyslipidemia, a condition marked by elevated LDL cholesterol and triglycerides along with low HDL cholesterol.
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Crestor is particularly effective in treating familial hypercholesterolemia, a genetic disorder resulting in significantly elevated cholesterol levels.
- Cardiovascular Risk Reduction: Crestor is prescribed to reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular events in patients with elevated cholesterol levels, especially those with additional risk factors such as diabetes or hypertension.
Dosage and Administration of Crestor
1. Dosage and Intake
- Hyperlipidemia and Mixed Dyslipidemia: The typical starting dose for managing hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia in adults is 10 mg to 20 mg once daily. Depending on the patient’s response and treatment goals, the dose may be increased to a maximum of 40 mg per day.
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia: For patients with familial hypercholesterolemia, the starting dose is usually 20 mg once daily. The dose may be adjusted based on the patient’s response and LDL cholesterol reduction goals.
2. Timing of Administration
- Regular Doses: Crestor should be taken once daily, at the same time each day, to maintain consistent medication levels in the body. It can be taken with or without food.
- Missed Dose: If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it is almost time for the next dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and continue with the regular dosing schedule.
3. Additional Recommendations
- With or Without Food: Crestor can be taken with or without food, offering flexibility in dosing.
- Avoid Grapefruit: Patients should avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking Crestor, as it can increase the risk of side effects.
Mechanism of Action of Crestor
1. Description of Mechanism
Crestor works by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme crucial for cholesterol production in the liver. This inhibition decreases cholesterol synthesis and increases the uptake and breakdown of LDL cholesterol.
2. Biochemical Processes
- Inhibition of HMG-CoA Reductase: By blocking this enzyme, Crestor reduces the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver, leading to lower blood cholesterol levels.
- Increased LDL Receptors: The reduction in cholesterol synthesis stimulates the liver to increase the number of LDL receptors, which helps clear LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
3. Physiological Effects
- Reduction of LDL Cholesterol: Lowering LDL cholesterol levels reduces the risk of plaque formation in the arteries, helping to prevent atherosclerosis.
- Increase in HDL Cholesterol: By increasing HDL cholesterol levels, Crestor helps protect against heart disease.
- Lowering of Triglycerides: Reducing triglyceride levels further contributes to a healthier lipid profile and reduces cardiovascular risk.
Composition of Crestor
1. General Introduction
Crestor is composed of both active and inactive ingredients that work together to provide its therapeutic effects.
2. Active Ingredients
- Rosuvastatin Calcium: The active component in Crestor, rosuvastatin calcium, is responsible for its cholesterol-lowering and cardiovascular protective effects.
3. Inactive Ingredients
- Excipients: These include substances such as lactose, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose, which help form the tablet and ensure its stability and efficacy.
Side Effects of Crestor
1. General Introduction
While Crestor is generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience side effects. Understanding these potential side effects helps in managing them effectively.
2. Possible Side Effects
- Common Side Effects: These include headache, muscle pain, abdominal pain, weakness, and nausea. These effects are typically mild and temporary.
- Less Common Side Effects: Some patients may experience joint pain, memory loss, or confusion.
3. Frequency and Severity
- Mild to Moderate: Most side effects are mild to moderate in severity and tend to diminish as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Severe: Rarely, severe side effects such as muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis) and liver damage can occur. Immediate medical attention is required in such cases.
Prevention of Side Effects
1. General Introduction
Preventing side effects involves careful adherence to the prescribed dosage and usage guidelines.
2. Tips to Prevent Side Effects
- Follow Dosage Instructions: Adhering to the prescribed dosage reduces the risk of side effects.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help alleviate muscle pain and cramps.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can exacerbate side effects, particularly those related to liver function.
3. Recommendations for Improving Tolerance
- Gradual Adjustment: Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help the body adjust.
- Report Adverse Effects: Reporting any adverse effects to a healthcare provider ensures timely management and adjustment of the treatment plan.
Contraindications for Crestor
1. General Introduction
Certain conditions and factors may contraindicate the use of Crestor.
2. Conditions and Diseases
- Pregnancy: Crestor is contraindicated during pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus.
- Liver Disease: Patients with active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations of liver enzymes should not use Crestor.
3. Warnings for Different Patient Groups
- Elderly Patients: Elderly patients may be more sensitive to the side effects of Crestor.
- Children: Use in children should be closely monitored by a healthcare provider, typically only for those with familial hypercholesterolemia.
Warnings and Precautions
1. General Introduction
Taking certain precautions can minimize the risks associated with Crestor use.
2. Important Warnings
- Avoid Operating Machinery: Due to its potential side effects, patients should avoid driving or operating heavy machinery after taking Crestor until they know how it affects them.
- Alcohol Interaction: Alcohol can increase the risk of liver damage and should be avoided or limited.
3. Measures for Minimizing Risks
- Monitor Side Effects: Regularly monitor for any adverse effects and report them to a healthcare provider.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular blood tests to monitor liver function and cholesterol levels are recommended during Crestor therapy.
Missed Dose
1. What to Do if a Dose is Missed
If a dose of Crestor is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless it is almost time for the next dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and continue with the regular dosing schedule.
2. Tips for Adhering to Dosing Schedule
- Set Reminders: Use alarms or reminders to ensure timely medication intake.
- Keep a Log: Maintain a log or chart to track dosing times and adherence.
Drug Interactions
1. Introduction
Crestor can interact with other medications, affecting its efficacy and safety.
2. Examples of Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Drugs such as cyclosporine, certain antibiotics, and antifungals can increase Crestor levels in the blood, raising the risk of side effects.
- Antacids: Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium can reduce the absorption of Crestor if taken simultaneously.
3. How to Avoid Negative Interactions
- Inform Healthcare Providers: Always inform healthcare providers about all medications being taken.
- Time Antacid Use: If antacids are needed, take them at least two hours after Crestor to avoid interaction.
Overdose
1. Symptoms of Overdose
Symptoms of a Crestor overdose can include severe muscle pain, weakness, fatigue, and in severe cases, kidney failure due to rhabdomyolysis.
2. Actions to Take in Case of Overdose
- Seek Immediate Medical Attention: Contact emergency services or go to the nearest emergency room immediately.
- Do Not Induce Vomiting: Unless instructed by a healthcare provider, do not attempt to induce vomiting.
Pharmacokinetics of Crestor
1. Absorption
Crestor is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 3 to 5 hours after oral administration.
2. Distribution
Rosuvastatin is extensively bound to plasma proteins and is distributed throughout the body, particularly in the liver, where it exerts its primary effect.
3. Metabolism
Crestor undergoes minimal metabolism, primarily in the liver, and is excreted largely unchanged in the feces.
4. Elimination
The drug is excreted primarily through the feces (about 90%) and to a lesser extent through the urine (about 10%). The elimination half-life of rosuvastatin is approximately 19 hours.
Dosage Forms
1. Available Forms and Dosages
Crestor is available in various forms, including tablets of 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, and 40 mg. This range of dosages allows for flexible dosing based on patient needs.
2. Advantages of Dosage Forms
- Tablets: Convenient for routine use and easy to dose accurately.
- Different Strengths: Allows for personalized dosing to achieve optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
1. Safety of Use
Crestor is contraindicated during pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus. It is also excreted in breast milk, so breastfeeding mothers should consult with a healthcare provider before use.
2. Recommendations for Pregnant and Nursing Mothers
- Consult Healthcare Provider: Always seek medical advice before starting or continuing Crestor during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Monitor Infant: If used during breastfeeding, monitor the infant for any adverse effects.
Storage Conditions
1. Storage Recommendations
Crestor should be stored at room temperature, away from light and moisture. Keep it out of reach of children and pets.
2. Temperature and Other Conditions
- Optimal Temperature: Store Crestor at a temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
- Avoid Humidity: Keep the medication in a dry place to maintain its efficacy.
Clinical Trials and Efficacy
1. Overview of Clinical Studies
Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of Crestor in treating hyperlipidemia, mixed dyslipidemia, and familial hypercholesterolemia. These studies confirm its effectiveness in reducing LDL cholesterol levels and lowering the risk of cardiovascular events.
2. Main Results and Findings
- Cholesterol Reduction: Crestor significantly reduces LDL cholesterol levels, often by up to 50%.
- Cardiovascular Risk Reduction: The incidence of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events is notably lower in patients treated with Crestor.
Conclusion
1. Summary of Crestor
Crestor is a versatile and highly effective medication for managing high cholesterol levels and reducing cardiovascular risk. Its benefits, including significant LDL cholesterol reduction and cardiovascular protection, make it an invaluable treatment option for many patients.
2. Main Benefits and General Recommendations
- Benefits: Crestor effectively lowers LDL cholesterol, reduces triglycerides, increases HDL cholesterol, and lowers cardiovascular risk.
- Recommendations: Follow prescribed dosages, regularly monitor for side effects, and consult healthcare providers to ensure optimal management of cholesterol levels and overall health.